Proficient in Python (Basic) - Flow Control Statements
posted on 2023-05-07 21:21 read(1163) comment(0) like(8) collect(0)
flow control statement
1️⃣Introduction
Computers have three organizational structures when executing code:
- Sequential structure: Programs are executed sequentially from top to bottom.
- Selection structure: select and execute different code blocks according to conditions.
- Loop structure: Repeatedly execute a certain block of code.
2️⃣Conditional judgment
If a program is followed step by step from beginning to end without turning points in the middle, it will not be able to complete too much work. Program design often requires a turning point, which is called flow control in programming.
⚜️ Relational Operators
Relational operators are often needed for comparisons in selection constructs and loop constructs.
The relational operators in Python are as follows ⬇️:
| relational operator | describe | example |
|---|---|---|
< | less than | a < b |
<= | less than or equal to | a <= b |
> | more than the | a > b |
>= | greater than or equal to | a >= b |
== | equal | a += b |
!= | not equal to | a != b |
The result returned by the operation is of boolean type. Returns True for True and False for False.
⚜️ Logical operators
- and: Both conditions are met. (and)
- or: satisfy condition 1 or satisfy condition 2. (or)
- not: The opposite of the conditional result. (No)
andThe following is a diagrammatic description of logical operators ⬇️:
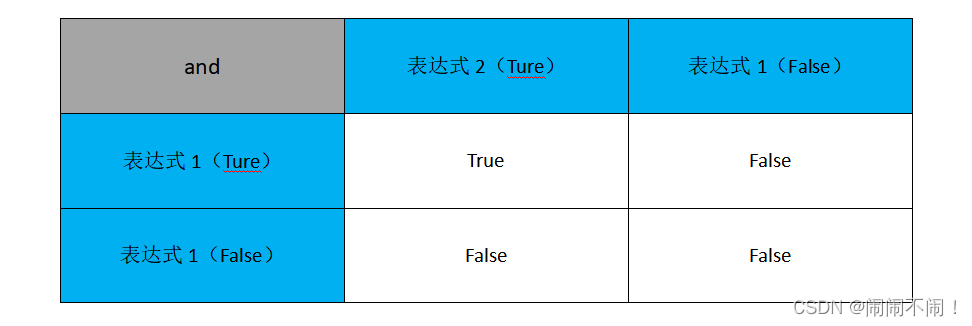
Cleverly remember the formula:one false is false
orThe following is a diagrammatic description of logical operators ⬇️:
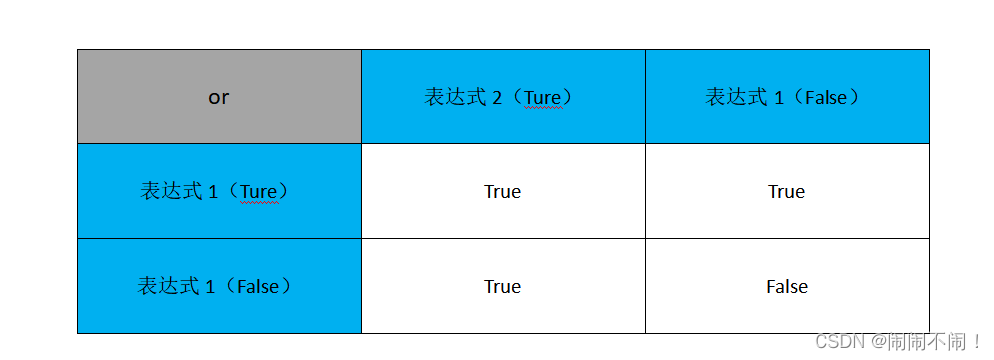
Cleverly remember the formula:true is true
The following is a textual description of the logical operators not⬇️:
If the expression is true (True), the result of the not expression is false (False); if the expression is false (False), the result of the not expression is true (True).
⚜️if statement
The basic syntax of an if statement is as follows ⬇️:
if (conditional judgment):
code block
If the result of the conditional expression is true, the statement is executed, and if it is false, it is skipped.
Case ⬇️
age = 18
if age == 18: # 判断18是否等于变量age中的值
print('您已经成年了。')
If the code block has only one statement it can be simplified:
if (conditional judgment): code block
Case ⬇️
age = 18
if age >= 18: print('您已经成年了。')
⚜️if...else statement
A more common situation in programming is to execute a block of code when a condition is judged to be true (True); to execute another block of code when the condition is false (False).
if... elseThis is where sentences are needed .
The basic syntax of the if...else statement is as follows ⬇️:
if (conditional judgment):
Code block 1
else:
Code block 2
Case ⬇️
age = 18
if age >= 18: # 判断条件,如果满足执行代码块1不满足执行代码块2
print('您已经成年了。')
else:
print('您还未成年。')
⚜️if...elif...else statement
When the program requires multiple conditional judgments, relying solely on if or if...else cannot meet our needs. This is the
if...elif...elsestatement we can use.
The basic syntax of the if... elif...else statement is as follows ⬇️:
if (conditional judgment):
Code block 1
elf:
Code block 2
…
else:
code block n
Case ⬇️
score = 93
if score >= 90:
print('您的成绩等级为A')
elif score >= 80:
print('您的成绩等级为B')
elif score >= 60:
print('您的成绩等级为C')
else:
print('您的成绩等级为D')
⚜️match…case
Python 3.10 adds the conditional judgment
match...caseof . The function is similar to the switch in the Java language.
Python3.10 installation package link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1S3o10uIyhjmIkVtDc_ae0g?pwd=h1ur
Extraction code: h1ur:
The basic syntax of the match...case statement is as follows ⬇️:
match (conditional judgment):
case value 1:
Code block 1
case value 2:
Code block 2
…
case _:
code block n
_match any result with a single underscore
Case ⬇️
score = 90
match score//10:
case 10,9:
print('您的成绩等级为A')
case 8:
print('您的成绩等级为B')
case 6,7:
print('您的成绩等级为C')
case _:
print('您的成绩等级为D')
3️⃣Loop structure
⚜️while
The four steps of the while loop are: initial value, loop condition, loop body, iteration
The basic syntax of the while loop is as follows ⬇️:
while (conditional judgment) :
code block
Case ⬇️
num = 1 # 1.赋初始值
sum = 0
while num <= 100: # 循环条件
sum += num # 循环体
num += 1 # 迭代更新,改变条件变量
print('1~100之间的累加和为:',sum)
⚜️while...else statement
When the condition is judged to be true (True), the code block in the loop is executed; when the condition is false (Flase), the code block in the else is executed.
The basic syntax of while...else is as follows ⬇️:
while (conditional judgment) :
Code block 1
else:
Code block 2
Case ⬇️
num = 1
sum = 0
while num <= 100:
sum += num
num += 1
else:
print('1~100之间的累加和为:',sum)
⚜️for
The basic syntax of a for loop is as follows ⬇️:
for (loop variable) in (traversal object):
code block
The traversal object can be: string, file, list, range function, etc.
Case ⬇️
for i in range(1,11,2):
print(i) # 打印1~10之间的奇数
⚜️for...else statement
When the condition is judged to be true (True), the code block in the loop is executed; when the condition is false (Flase), the code block in the else is executed.
The basic syntax of for...else is as follows ⬇️:
for loop variable in (traversal object):
Code block 1
else:
Code block 2
Case ⬇️
for i in range(1,11,2):
print(i) # 打印1~10之间的奇数
else:
print('程序结束')
4️⃣ Exit the loop
⚜️continue
If you want to skip the loop when certain conditions occur, you can use it at this time
continue, and continue generally needs to be used with if.
The basic syntax of continue is as follows ⬇️:
for (loop variable) in (traversal object):
code block
if (conditional judgment): # If the condition is true, exit this loop
continue
Case ⬇️
for i in range(1,11):
if i % 2 == 0: # 如果i是偶数跳过
continue
print(i) # 打印1~10之间的奇数
⚜️break
If you want to exit the entire loop when certain conditions occur, you can use it at this time
break, and break also needs to be used in conjunction with if.
The basic syntax of break is as follows ⬇️:
for (loop variable) in (traversal object):
code block
if (conditional judgment): # If the condition is true, exit the loop
break
Case ⬇️
for i in range(1,11,2):
print(i) # 打印1~10之间的奇数
if i == 7: # 当i等于7时提前退出循环
break
Note: In the case of for...else or while...else, use break, the statement after else will not be executed.
Category of website: technical article > Blog
Author:kkkkkkkkkkdsdsd
link:http://www.pythonblackhole.com/blog/article/379/39bb23523fb0028fe320/
source:python black hole net
Please indicate the source for any form of reprinting. If any infringement is discovered, it will be held legally responsible.
name:
Comment content: (supports up to 255 characters)
no articles