classification
no classification
tag
no tag
date
no datas
2021 The 12th Blue Bridge Cup Provincial Competition Python University Group real questions plus analysis (updating)
posted on 2023-05-07 20:06 read(560) comment(0) like(6) collect(2)
Table of contents
3. Question C: Cargo placement
8. Question H: Left Child Right Brother
13. The Wounded Queen (2021 Mock Questions)
16. Irrigation (simulation competition questions)
22. Time addition (simulation questions)
1. Question A: Cards

Idea: There are 2021 numbers for each number from 0 to 9, and 1 is definitely the fastest to use, which is to calculate a total of 2021 numbers between 1 and a certain number 1
code:
- s=0
- for i in range(1,5000):
- s=s+str(i).count('1')
- if s==2021:
- print(i)
- break
Final answer: 3181
2. Question B: Straight line

Idea: (Boring ideas from others) At the beginning, I was still thinking about how to use the form of y=kx+b to represent a straight line. There is no way to find the slope of a vertical line in this form, and special circumstances must be considered. Later, I saw a big guy on the Internet saying that a two-point straight line equation can be used:(y1-y2) * x +(x2-x1) * y +( x1 * y2 - x2 * y1)=0
The final calculated result is Ax+By+C=0in the format, as long as A, B, and C after the reduction are not the same, they can be regarded as different straight lines.
code:
- dian=[]
- for i in range(0,20):
- for j in range(0,21):
- dian.append((i,j))
- result=set()
- def gys(x,y):#求x,y的最大公约数
- if y==0:
- return x
- return gys(y,x%y)
-
- for i in range(len(dian)-1):
- x1,y1=dian[i]
- for j in range(i+1,len(dian)):
- x2,y2=dian[j]
- a=y1-y2
- b=x2-x1
- c=x1*y2-x2*y1
- k=gys(gys(a,b),c)
- result.add((a/k,b/k,c/k))
-
- print(len(result))

The set() collection itself has the characteristic of not repeating.
For the set() collection, adding elements to it should use the add function. Distinct from append.
3. Question C: Cargo placement

Idea: L, W, and H are all factors of n, so first find all the factors of n and put them in the sequence. Then perform a three-layer loop on all the numbers in the sequence to see how many schemes meet the conditions.
code:
- import math
- n = 2021041820210418
- fac = []
- for i in range(1, int(math.sqrt(n)) + 1):
- if n % i == 0:
- fac.append(i)
- fac.append(int(n / i))
-
- x = 0
- for l in fac:
- for k in fac:
- for m in fac:
- if l * k * m == n:
- x = x + 1
- print(x)

4. Question D: Path

Ideas: This question adopts the idea of dynamic programming. dp[i] represents the shortest path length between node 1 and node i.
code:
- dp=[float('inf')]*2022
-
- def gbs(x,y):#求x和y的最小公倍数
- x1=x
- y1=y
- while y:
- x,y=y,x%y
- return (x1*y1//x)
-
- for i in range(1,22):
- dp[i]=i
-
- for i in range(22,2022):
- for j in range(1,22):
- dp[i]=min(dp[i],dp[i-j]+gbs(i,i-j))
-
- print(dp[2021])

Answer: 10266837
5. Loop count

6. Question F: Time display


code:
- n=int(input())
- a=24*60*60*1000
- c=n%a
- hour=c//(60*60*1000)
- minu=(c%(60*60*1000))//(60*1000)
- sec=(c%(60*1000))//1000
- print('%02d'%hour,end=':')
- print('%02d'%minu,end=':')
- print('%02d'%sec,end='')
7. Question G: Yang Hui Triangle

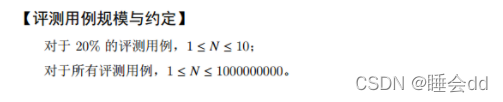
Ideas for reference: (156 messages) Preparing for the Blue Bridge Cup Over the Years Exam Questions: Yang Hui Triangular Provincial Competition Group B Python Detailed Explanation_m0_62277756's Blog-CSDN Blog
code:
- n=int(input())
-
- def c(a,b):
- res=1
- i,j=a,1
- while j<=b:
- res=res*i/j
- i-=1
- j+=1
- return int(res)
-
- def find(j,n):
- l=2*j
- r=n
- while l<=r:
- mid=(l+r)//2
- if c(mid,j)==n:
- print(int(mid*(mid+1)/2)+j+1)
- return True
- elif c(mid,j)>n:
- r=mid-1
-
- else:
- l=mid+1
- return False
-
-
- for i in range(16,-1,-1):
- if find(i,n):
- break

8. Question H: Left Child Right Brother

Code: (successful operation, the code is posted by someone else on the Lanqiao official website)
- import sys
- sys.setrecursionlimit(1000000)
- n=int(input())
- global ans
- ans=0
- def dfs(u):
- global ans
- tot=len(s[u])
- for i in range(tot):
- v=s[u][i]
- f[v]=f[u]+tot
- ans=max(ans,f[v])
- dfs(v)
- s=[[] for i in range(n+1)]
- f=[0]*(n+1)
- for i in range(n-1):s[int(input())].append(i+2)
- dfs(1)
- print(ans)

9. Question I: XOR Sequence


10. Item J: Bracket Sequence

11. Space

This is quite simple: 1MB=1024KB 1KB=1024B 1B=8bit
code:
- a=256*1024*1024*8//32
- print(a)
12. Jump
topic description
Xiaolan plays a game in a grid with n rows and m columns.
At the beginning, Xiaolan is standing in the upper left corner of the grid, which is row 1 and column 1.
Xiaolan can walk on the grid chart. When walking, if he is currently at row r and column c, he cannot go to a row with a row number smaller than r, nor can he go to a column with a column number smaller than c. At the same time, the straight-line distance he walks in one step does not exceed 3.
For example, if Xiaolan is currently at row 3, column 5, he can go to row 3, column 6, row 3, column 7, row 3, column 8, row 4, column 5, row 4 One of row 6, row 4, column 7, row 5, column 5, row 5, column 6, row 6, column 5.
Xiaolan will eventually go to the nth row and the mth column.
In the picture, some positions have rewards, which can be obtained by walking up, and some positions have punishments, which must be accepted by walking up. The reward and punishment are finally abstracted into a weight, the reward is positive, and the punishment is negative.
Xiaolan hopes that after going from row 1, column 1 to row n, column m, the total weight sum is the largest. What is the maximum?
enter description
The first line of input contains two integers n, m, denoting the size of the graph.
The next n lines, each with m integers, represent the weight of each point in the grid.
其中,1≤n≤100,−10**4≤权值≤10**4。
输出描述
输出一个整数,表示最大权值和。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
- 3 5
- -4 -5 -10 -3 1
- 7 5 -9 3 -10
- 10 -2 6 -10 -4
输出
15
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
思路:这个题采用动态规划的思想来解答,跟这篇文章上面第四题路径那个题目是差不多的。
做这个题目我认为有两点比较重要。一是想明白初始条件,二是确定状态转移方程。
通过读题,我们得到的题目条件为:如下图,从白点区域可以一步跳到对勾区域。

因此反过来说也就是:对于下面这个图,想要去到白点区域,可以从这些对勾区域一步跳过去。
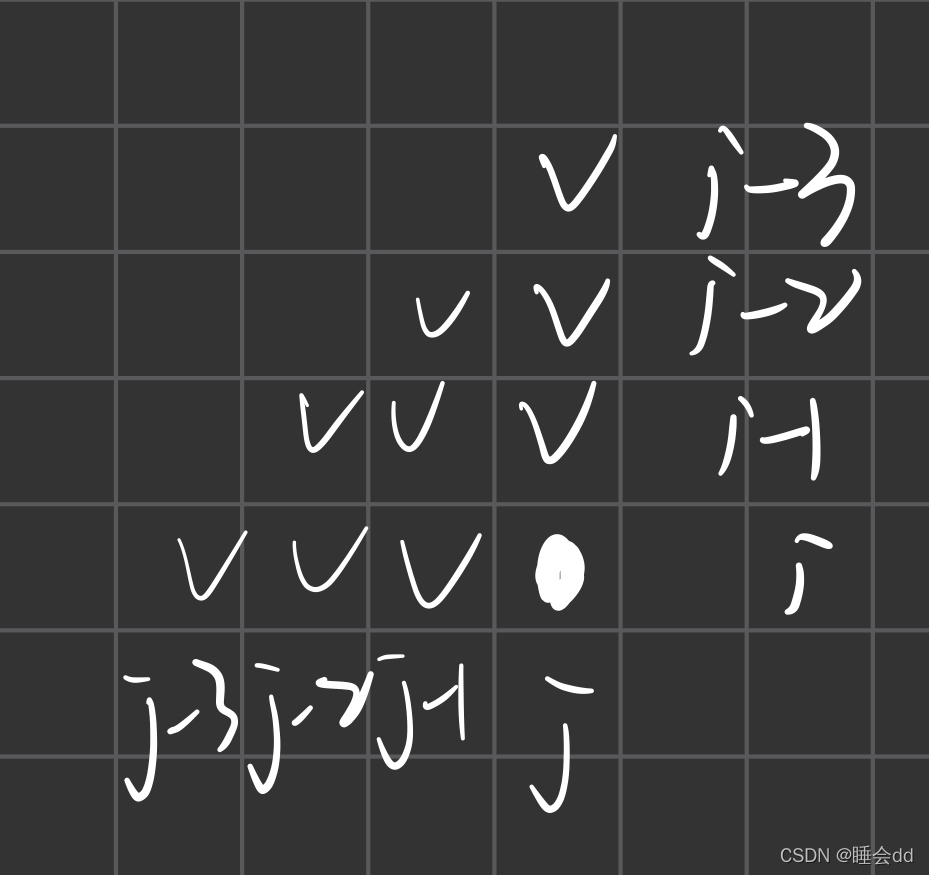
假设题目所给的各个点的权值存储在w这个二位列表当中,二维列表dp存储的是从第一行第一列那个点走到当前点的最大值。
那么初始条件dp[0][0]=w[0][0]
然后就是确定状态转移方程:dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j],dp[i-1][j-b])
代码:
- n,m=map(int,input().split())
- w=[]
- for i in range(n):
- w.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
- dp=[[0 for i in range(m)] for j in range(n)]
- dp[0][0]=w[0][0]
- for i in range(0,n):
- for j in range(0,m):
- for a in range(0,4):
- for b in range(0,4-a):
- if i-a>=0 and j-b>=0:
- dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j],dp[i-a][j-a]+w[i-a][j-a])
- print(dp[n-1][m-1])
这个题的代码我是仿照第四题来写的,第四题的初始条件是前22个数的dp都是直接赋值,1和那个数的最小公倍数。我做这个题也没多想,一开始直接把起点能一步跳过去的位置的dp值全都赋值w了,后来一想不对。人家第四题本身就是经过思考,确定了前22个数的dp就是1和它本身的最小公倍数,这就是最优解,才赋值的。。这个题的w可是有正有负,又没让求步数最小,还没准跳几步才能得到权值最小值呢。
13. 受伤的皇后(2021模拟题)
题目描述
有一个 n×n 的国际象棋棋盘(n 行n 列的方格图),请在棋盘中摆放 n 个受伤的国际象棋皇后,要求:
- 任何两个皇后不在同一行。
- 任何两个皇后不在同一列。
- 如果两个皇后在同一条 45 度角的斜线上,这两个皇后之间行号的差值至少为 3 。
请问一共有多少种摆放方案。
输入描述
输入的第一行包含一个整数 n。
其中,1≤n≤10。
输出描述
输出一个整数,表示答案。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
4
输出
2
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
代码:这个代码我是看的蓝桥官网上的的一个题解代码
- n=int(input())
- b=0
- def queen(A,row=0):
- global b
- if row==len(A):
- b+=1
- else:
- for wid in range(len(A)):
- A[row]=wid
- flag=True
- for hei in range(row):
- if wid==A[hei]:
- flag=False
- elif abs(hei-row)==abs(wid-A[hei]):
- if abs(hei-row)<3:
- flag=False
- if flag:
- queen(A,row+1)
-
- queen([None]*n)
- print(b)

思路解析:A是一个含有n个数的一维列表,Ai=a表示第i行的皇后放在这一行第a列的位置。这样在检查皇后排列的时候,检查是否皇后在同一列这个限制条件就特别方便。
14. 删除字符
题目描述
给定一个单词,请问在单词中删除 t个字母后,能得到的字典序最小的单词是什么?
输入描述
输入的第一行包含一个单词,由大写英文字母组成。
第二行包含一个正整数 t。
其中,单词长度不超过 100,t 小于单词长度。
输出描述
输出一个单词,表示答案。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
- LANQIAO
- 3
输出
AIAO
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
思路:用贪心思想来做,题目让删除t个字母,每次删除一个字母得到当前字典序最小的单词都是下一步删除字母的中间过程。
对于删除哪个字母,对于该单词从前往后遍历,只要左边字母的字典序大于右边字母的字典序,那么就删除这个左边字母。
代码:
- s=list(input())
- t=int(input())
-
- for j in range(t):
- index=0
- while s[index]<=s[index+1]:
- index=index+1
-
- s.remove(s[index])
- print(''.join(s))
-
-
15. 相乘
本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。
小蓝发现,他将 1至 1000000007 之间的不同的数与 2021相乘后再求除以 1000000007 的余数,会得到不同的数。 小蓝想知道,能不能在 1 至 1000000007 之间找到一个数,与 2021 相乘后 再除以 1000000007 后的余数为 999999999。如果存在,请在答案中提交这个数; 如果不存在,请在答案中提交 0。
这个就比较简单,直接暴力求解
代码:
- for i in range(1,1000000008):
- if i*2021%1000000007==999999999:
- print(i)
- break
-
16. 灌溉(模拟赛赛题)
题目描述
小蓝负责花园的灌溉工作。
花园可以看成一个 n 行 m 列的方格图形。中间有一部分位置上安装有出水管。
小蓝可以控制一个按钮同时打开所有的出水管,打开时,有出水管的位置可以被认为已经灌溉好。
每经过一分钟,水就会向四面扩展一个方格,被扩展到的方格可以被认为已经灌溉好。即如果前一分钟某一个方格被灌溉好,则下一分钟它上下左右的四个方格也被灌溉好。
给定花园水管的位置,请问 kk 分钟后,有多少个方格被灌溉好?
输入描述
输入的第一行包含两个整数 n,m。
第二行包含一个整数 t,表示出水管的数量。
接下来 t 行描述出水管的位置,其中第 i 行包含两个数 r,c 表示第r行第c 列有一个排水管。
接下来一行包含一个整数 k。
其中,1≤n,m≤100,1≤t≤10,1≤k≤100。
输出描述
输出一个整数,表示答案。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
- 3 6
- 2
- 2 2
- 3 4
- 1
输出
9
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
这个题比较简单就是用枚举来做
代码:
- n,m=map(int,input().split())
- t=int(input())
- s=[[0 for i in range(m)] for j in range(n)]
- s1=[[0 for i in range(m)] for j in range(n)]
- for i in range(t):
- x,y=map(int,input().split())
- s[x-1][y-1]=1
-
- k=int(input())
- for i in range(k):
- for a in range(n):
- for b in range(m):
- if s[a][b]==1:
- s1[a][b]=1
- if a>0:
- s1[a-1][b]=1
- if b>0:
- s1[a][b-1]=1
- if a<n-1:
- s1[a+1][b]=1
- if b<m-1:
- s1[a][b+1]=1
-
- s=s1
- print(sum([sum(i) for i in s]))

17. 扫雷
题目描述
在一个 n 行 m 列的方格图上有一些位置有地雷,另外一些位置为空。
请为每个空位置标一个整数,表示周围八个相邻的方格中有多少个地雷。
输入描述
输入的第一行包含两个整数 n,m。
第 2 行到第 n+1 行每行包含 m 个整数,相邻整数之间用一个空格分隔。如果对应的整数为 0,表示这一格没有地雷。如果对应的整数为 1,表示这一格有地雷。
其中,1≤n,m≤100 分钟后还是在当天。
输出描述
输出 n 行,每行 m 个整数,相邻整数之间用空格分隔。
对于没有地雷的方格,输出这格周围的地雷数量。对于有地雷的方格,输出 9。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
- 3 4
- 0 1 0 0
- 1 0 1 0
- 0 0 1 0
输出
- 2 9 2 1
- 9 4 9 2
- 1 3 9 2
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
这个题也很简单,直接两层循环就好
- a,b=map(int,input().split())
- s=[]
- for i in range(a):
- s.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
-
- ans=[[0 for i in range(b)] for j in range(a)]
- for i in range(a):
- for j in range(b):
- if s[i][j]==1:
- ans[i][j]=9
- else:
- tmp=0
- for ii in range(-1,2):
- for jj in range(-1,2):
- if i+ii>=0 and i+ii<a and j+jj>=0 and j+jj<b:
- tmp=tmp+s[i+ii][j+jj]
- ans[i][j]=tmp
- for i in range(a):
- for j in range(b):
- print(ans[i][j],end=' ')
- print()

18. 双向排序
题目描述
给定序列(a1,a2,⋅⋅⋅,an)=(1,2,⋅⋅⋅,n),即 ai=i。
小蓝将对这个序列进行 m 次操作,每次可能是将 a1,a2,⋯,aqi 降序排列,或者将 aqi,aqi+1,⋯,an 升序排列。
请求出操作完成后的序列。
输入描述
输入的第一行包含两个整数 n,m,分别表示序列的长度和操作次数。
接下来 m 行描述对序列的操作,其中第 i 行包含两个整数 pi,qi 表示操作类型和参数。当 pi=0 时,表示将 a1,a2,⋅⋅⋅,aqi 降序排列;当 pi=1 时,表示将 aqi,aqi+1,⋯,an 升序排列。
输出描述
输出一行,包含 n 个整数,相邻的整数之间使用一个空格分隔,表示操作完成后的序列。
输入输出样例
示例
输入
- 3 3
- 0 3
- 1 2
- 0 2
输出
3 1 2
样例说明
原数列为(1,2,3)。
第 1 步后为(3,2,1)。
第 2 步后为(3,1,2)。
第 3 步后为(3,1,2)。与第 2 步操作后相同,因为前两个数已经是降序了。
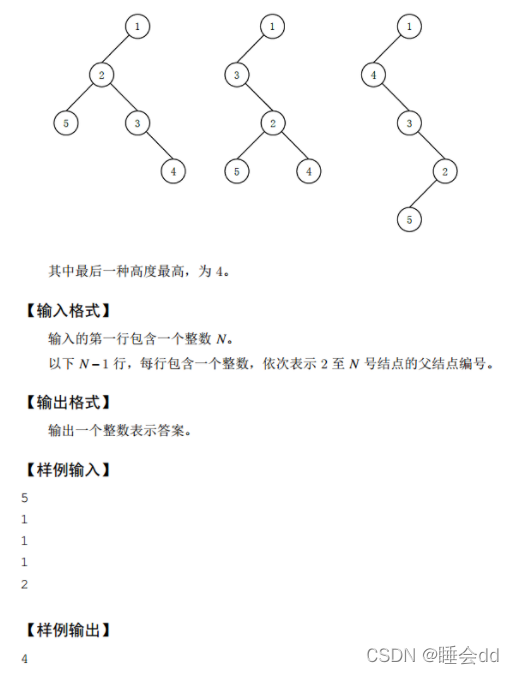
评测用例规模与约定
对于 30% 的评测用例,n,m≤1000;
对于 60% 的评测用例,n,m≤5000;
对于所有评测用例,1≤n,m≤100000,0≤pi≤1,1≤qi≤n。
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:2s
- 最大运行内存: 256M
这个题我用python本身自带的sort函数进行排序的话,时间会超限
下面是时间超限的代码:
- n,m=map(int,input().split())
- s=[]
- for i in range(m):
- p,q=map(int,input().split())
- s.append((p,q))
- l=[i for i in range(1,n+1)]
- for i in range(m):
- p,q=s[i]
- if p==0:
- tmp=l[0:q]
- tmp.sort(reverse=True)
- l=tmp+l[q:]
- else:
- tmp=l[q-1:]
- tmp.sort()
- l=l[0:q-1]+tmp
- for i in range(n):
- print(l[i],end=' ')
-

这个题我在蓝桥杯练习系统没看到有人发布python的题解,,先这样。。后续找到了在更新。
19. 谈判
题目描述
在很久很久以前,有 n 个部落居住在平原上,依次编号为 1 到 n。第 i 个部落的人数为 ti。
有一年发生了灾荒。年轻的政治家小蓝想要说服所有部落一同应对灾荒,他能通过谈判来说服部落进行联合。
每次谈判,小蓝只能邀请两个部落参加,花费的金币数量为两个部落的人数之和,谈判的效果是两个部落联合成一个部落(人数为原来两个部落的人数之和)。
输入描述
输入的第一行包含一个整数 n,表示部落的数量。
第二行包含 n 个正整数,依次表示每个部落的人数。
其中,1≤n≤1000,1≤ti≤104。
输出描述
输出一个整数,表示最小花费。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
- 4
- 9 1 3 5
输出
31
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
思路:这个也很简单,每次找人数最少的两个部落进行谈判即可
代码:
- n=int(input())
- s=list(map(int,input().split()))
- result=0
- s.sort()
- for i in range(n-1):
- ans=s[0]+s[1]
- result=result+ans
- s.pop(0)
- s.pop(0)
- s.append(ans)
- s.sort()
-
- print(result)
20.最少砝码
这个我之前写过题解:
(142条消息) 蓝桥杯备赛:贪心_睡会dd的博客-CSDN博客
21. 距离和
题目描述
本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。
两个字母之间的距离定义为它们在字母表中位置的距离。例如 A 和 C 的距离为 2,L 和 Q 的距离为 5。
对于一个字符串,我们称字符串中两两字符之间的距离之和为字符串的内部距离。
例如:ZOO 的内部距离为 22,其中 Z 和 O 的距离为 11。
请问,LANQIAO 的内部距离是多少?
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
代码:
- s='LANQIAO'
- ans=0
- for i in range(6):
- for j in range(i+1,7):
- ans=abs(ord(s[i])-ord(s[j]))+ans
-
- print(ans)
-
这个题很简单,唯一需要记住的是ord函数以一个字符(长度为1的字符串)作为参数,返回对应的 ASCII 数值,或者 Unicode 数值。
同时提一下chr函数,chr() 用一个范围在 range(256)内的(就是0~255)整数作参数,返回一个对应的字符。
22.时间加法(模拟题)
题目描述
现在时间是 a 点 b 分,请问 t 分钟后,是几点几分?
输入描述
输入的第一行包含一个整数 a。
第二行包含一个整数 b。
第三行包含一个整数 t。
其中0≤a≤23,0≤b≤59,0≤t,t 分钟后还是在当天。
输出描述
输出第一行包含一个整数,表示结果是几点。
第二行包含一个整数,表示结果是几分。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
- 3
- 20
- 165
输出
- 6
- 5
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
代码:
- a=int(input())
- b=int(input())
- t=int(input())
- a=a+(b+t)//60
- if a>23:
- a=a-24
- b=(b+t)%60
- print(a)
- print(b)
23. 排列小球
题目描述
小蓝有黄绿蓝三种颜色的小球,分别为 R,G,B 个。同样颜色的小球没有区别。
小蓝将这些小球从左到右排成一排,排完后,将最左边的连续同色小球个数记为 t1,将接下来的连续小球个数记为 t2,以此类推直到最右边的小球。
请问,总共有多少总摆放小球的方案,使得 t1,t2,⋯ 为严格单调递增序列,即 t1≤t2≤t3≤⋯。
输入描述
输入一行包含三个整数 R,G,B。
其中,0≤R,G,B≤50。。
输出描述
输出一个整数,表示答案。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
3 6 0
输出
3
样例说明
用 r 表示红球,g 表示绿球,可能的方案包括:
rrrgggggg
grrrggggg
ggrrrgggg
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
代码:这个是看的蓝桥官网别人发的
- r,g,b=[int(x)for x in input().split(' ')]
-
- S=0
- def dfs(r,g,b,i,c):
- global S
- if r==0 and g==0 and b==0:
- S+=1
- return True
- if r>i and c!='r':
- for j in range(i,r+1):
- if j>i:
- dfs(r-j,g,b,j,'r')
- if g>i and c!='g':
- for j in range(i,g+1):
- if j>i:
- dfs(r,g-j,b,j,'g')
- if b>i and c!='b':
- for j in range(i,b+1):
- if j>i:
- dfs(r,g,b-j,j,'b')
- return False
-
-
- dfs(r,g,b,0,'')
- print(S)

24. 序列个数
题目描述
本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。
请问有多少个序列满足下面的条件:
- 序列的长度为 5。
- 序列中的每个数都是 1 到 10 之间的整数。
- 序列中后面的数大于等于前面的数。
代码:
- count=0
- for a in range(1,11):
- for b in range(a,11):
- for c in range(b,11):
- for d in range(c,11):
- for e in range(d,11):
- count+=1
-
- print(count)
答案:2002
25. 合法日期
题目描述
小蓝正在上小学,老师要求同学们在暑假每天记日记。可是小蓝整个暑假都在玩,直到最后一天才想起要记日记。于是小蓝赶紧编了一些日记交给老师。
没想到,日记很快就被老师发现了问题,原来小蓝记完 8 月 31 日的日记,竟又记了 8 月 32 日和 8 月 33 日的日记。这显然是有问题的,因为根本没有 8 月 32 日和 8 月 33 日。
给定一个月份和一个日期,请问 2021 年有没有这一天。
输入描述
输入的第一行包含一个整数 m,表示月份。
第二行包含一个整数 d,表示日期。
其中,1≤m≤20,1≤d≤40。
输出描述
如果2021年有 m 月 d 日,输入 yes,否则输出 no。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
- 8
- 32
输出
no
示例 2
输入
- 2
- 28
输出
yes代码:
- import datetime
- m=int(input())
- d=int(input())
- try:
- a=datetime.date(2021,m,d)
- print('yes')
- except:
- print('no')
这次用到了datetime模块,把这个模块的其他函数也学习一下:
Python datetime模块详解 - Awakenedy - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
26. 图像模糊
题目描述
小蓝有一张黑白图像,由 n×m 个像素组成,其中从上到下共 n 行,每行从左到右 m 列。每个像素由一个 0 到 255 之间的灰度值表示。
现在,小蓝准备对图像进行模糊操作,操作的方法为:
对于每个像素,将以它为中心 3×3 区域内的所有像素(可能是 9 个像素或少于 9 个像素)求和后除以这个范围内的像素个数(取下整),得到的值就是模糊后的结果。
请注意每个像素都要用原图中的灰度值计算求和。
输入描述
输入的第一行包含两个整数 n,m。
第 2 行到第n+1 行每行包含 m 个整数,表示每个像素的灰度值,相邻整数之间用一个空格分隔。
其中,1≤n,m≤100 。
输出描述
输出 n 行,每行 m 个整数,相邻整数之间用空格分隔,表示模糊后的图像。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
- 3 4
- 0 0 0 255
- 0 0 255 0
- 0 30 255 255
输出
- 0 42 85 127
- 5 60 116 170
- 7 90 132 191
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
代码:
- import math
- n,m=map(int,input().split())
- s=[]
- for i in range(n):
- s.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
- s1=[[0 for i in range(m)] for j in range(n)]
- for i in range(n):
- for j in range(m):
- count=1
- tmp=s[i][j]
- if i-1>=0 and j-1>=0:
- count=count+1
- tmp=tmp+s[i-1][j-1]
- if i-1>=0 and j>=0:
- count=count+1
- tmp=tmp+s[i-1][j]
- if i-1>=0 and j+1<=m-1:
- count=count+1
- tmp=tmp+s[i-1][j+1]
- if j-1>=0:
- count=count+1
- tmp=tmp+s[i][j-1]
- if j+1<=m-1:
- count=count+1
- tmp=tmp+s[i][j+1]
- if i+1<=n-1 and j-1>=0:
- count=count+1
- tmp=tmp+s[i+1][j-1]
- if i+1<=n-1 :
- count=count+1
- tmp=tmp+s[i+1][j]
- if i+1<=n-1 and j+1<=m-1:
- count=count+1
- tmp=tmp+s[i+1][j+1]
- s1[i][j]=math.floor(tmp/count)
-
- for i in range(n):
- for j in range(m):
- print(s1[i][j],end=' ')
- print()

python取整函数:
向上取整:math.ceil()
四舍五入:round()
向下取整:math.floor()
向0取整:int()
27. 数字位数
题目描述
本题为填空题,只需要算出结果后,在代码中使用输出语句将所填结果输出即可。
整数 1 到 6 连在一起,成为 123456,长度为 6。
整数 1 到 12 连在一起,成为 123456789101112,长度为 15。
请问整数 1 到 2020 连在一起,长度为多少?
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 128M
- count=0
- for i in range(1,2021):
- count=count+len(str(i))
- print(count)
28. 时间显示
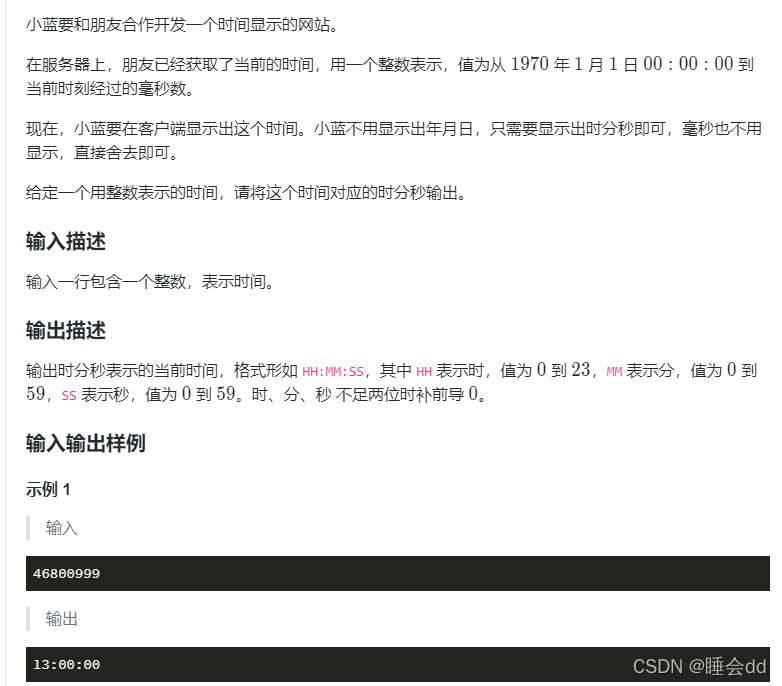
代码:
- from datetime import datetime,timedelta
- start=datetime(year=1970,month=1,day=1)
- dela=timedelta(milliseconds=1)
- now=int(input())
- now=start+now*dela
- print("%02d:%02d:%02d"%(now.hour,now.minute,now.second))
Category of website: technical article > Blog
Author:python98k
link:http://www.pythonblackhole.com/blog/article/327/191727f62a2e1fdcbaa3/
source:python black hole net
Please indicate the source for any form of reprinting. If any infringement is discovered, it will be held legally responsible.
name:
Comment content: (supports up to 255 characters)