Python爬虫大作业+数据可视化分析(抓取python职位)
posted on 2023-05-21 17:33 read(1049) comment(0) like(24) collect(0)
Table of contents
2. Obtain web page information
3. Use flask to realize visualization
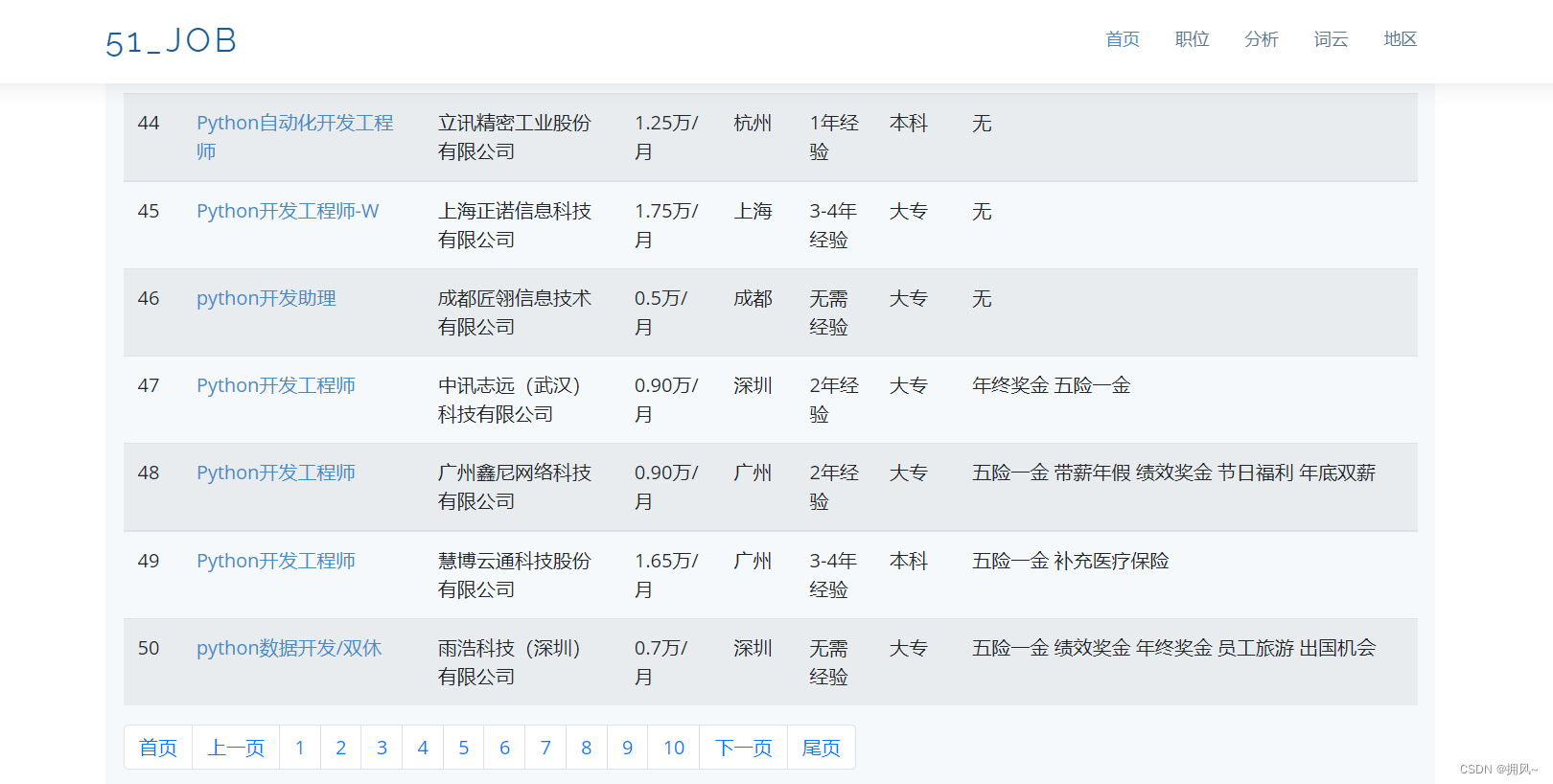
2.1 Job information display + pagination
1. Obtain data
Use regular expressions to find the corresponding data, then clean the data, and finally save the data, save it as an excel file and save it in the database. (The sqlite database is used here)
1. Import related libraries
- import re # 正则表达式,进行文字匹配
- from urllib.request import Request
- from urllib.request import urlopen # 制定URL,获取网页数据
- from urllib.error import URLError as error
- import json
- import xlwt
- import sqlite3
2. Obtain web page information
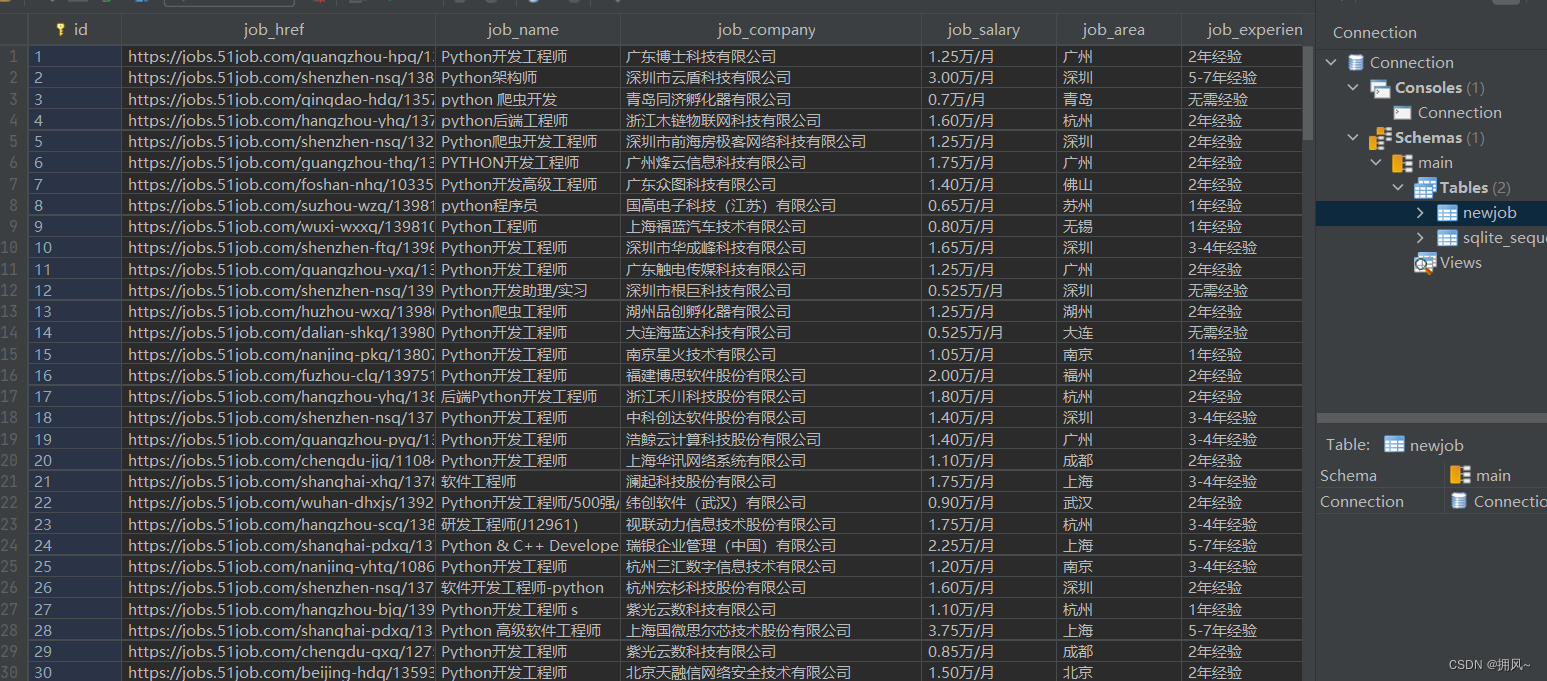
There are a lot of information crawled, which need to be matched with regular expressions. A job has: 8 attributes. I only crawl job title, company name, company link, salary, work location, whether it is an internship, and employee treatment.
- def main():
- baseurl = "https://search.51job.com/list/000000,000000,0000,00,9,99,python,2,{}.html?lang=c&postchannel=0000&workyear=99&cotype=99°reefrom=99&jobterm=99&companysize=99&ord_field=0&dibiaoid=0&line=&welfare="
- # 1.爬取网页
- datalist = getData(baseurl)
- savepath = "51job.xls"
- jobpath = "newjob.db"
- # 保存数据到表格
- saveData(datalist, savepath)
- # 保存数据到数据库
- saveData2DB(datalist, jobpath)
-
-
- # 爬取网页
- def getData(baseurl):
- datalist = []
- for page in range(0, 30):
- url1 = baseurl.format(page + 1)
- html = askURL(url1) # 保存获取到的网页源码
- # 2.逐一解析数据
- html_data = re.findall('window.__SEARCH_RESULT__ =(.*?)</script>', html, re.S)
- html_data = ''.join(html_data)
- infodict = json.loads(html_data) # 将str类型的数据转换为dict类型
- engine_jds = infodict['engine_jds']
- for item in engine_jds:
- data = []
- job_href = item["job_href"] # 工作链接
- name = item['job_name']
-
- temp1 = re.sub('\t', '', name)
- # 去掉括号中的内容,英文的括号要加反斜杠
- temp2 = re.sub('\(.*?\)', '', temp1)
- # 去掉括号中的内容,中文括号
- job_name = re.sub('(.*?)', '', temp2)
-
- job_company = item['company_name']
- job_salary1 = item['providesalary_text']
- if job_salary1:
- job_salary = get_avgsalary(job_salary1)
- else:
- job_salary = ""
- area = item["workarea_text"] # 工作地点
- newarea = re.findall('(.*?)-', area, re.S)
- job_area = ''.join(newarea)
- demand = item['attribute_text'][1:]
- job_requirements = ' '.join(demand)
- if job_requirements.find(' ') != -1:
- job_experience, job_education = job_requirements.split(' ')
- else:
- job_experience = job_requirements
- job_fuli = item['jobwelf'] if item['jobwelf'] else '无'
- if job_salary == "" or job_area == "" or job_education == "":
- continue
- else:
- data.append(job_href)
- data.append(job_name)
- data.append(job_company)
- data.append(job_salary)
- data.append(job_area)
- # data.append(job_requirements)
- data.append(job_experience)
- data.append(job_education)
- data.append(job_fuli)
- datalist.append(data)
- # print(datalist)
- return datalist

3. Data cleaning
The salary is mainly cleaned, and the unit is 10,000/month, and the average value of the interval is taken.
- # 对薪资进行数据清洗
- def get_avgsalary(salary):
- global avg_salary
- if '-' in salary: # 针对10-20千/月或者10-20万/年的情况,包含-
- low_salary = re.findall(re.compile('(\d*\.?\d+)'), salary)[0]
- high_salary = re.findall(re.compile('(\d?\.?\d+)'), salary)[1]
- avg_salary = (float(low_salary) + float(high_salary)) / 2
- avg_salary = ('%.2f' % avg_salary)
- if u'万' in salary and u'年' in salary: # 单位统一成万/月的形式
- avg_salary = float(avg_salary) / 12
- avg_salary = ('%.2f' % avg_salary) # 保留两位小数
- elif u'千' in salary and u'月' in salary:
- avg_salary = float(avg_salary) / 10
- else: # 针对20万以上/年和100元/天这种情况,不包含-,取最低工资,没有最高工资
- avg_salary = re.findall(re.compile('(\d*\.?\d+)'), salary)[0]
- if u'万' in salary and u'年' in salary: # 单位统一成万/月的形式
- avg_salary = float(avg_salary) / 12
- avg_salary = ('%.2f' % avg_salary)
- elif u'千' in salary and u'月' in salary:
- avg_salary = float(avg_salary) / 10
- elif u'元' in salary and u'天' in salary:
- avg_salary = float(avg_salary) / 10000 * 21 # 每月工作日21天
-
- avg_salary = str(avg_salary) + '万/月' # 统一薪资格式
- return avg_salary

4. Crawl results:
2. Save data
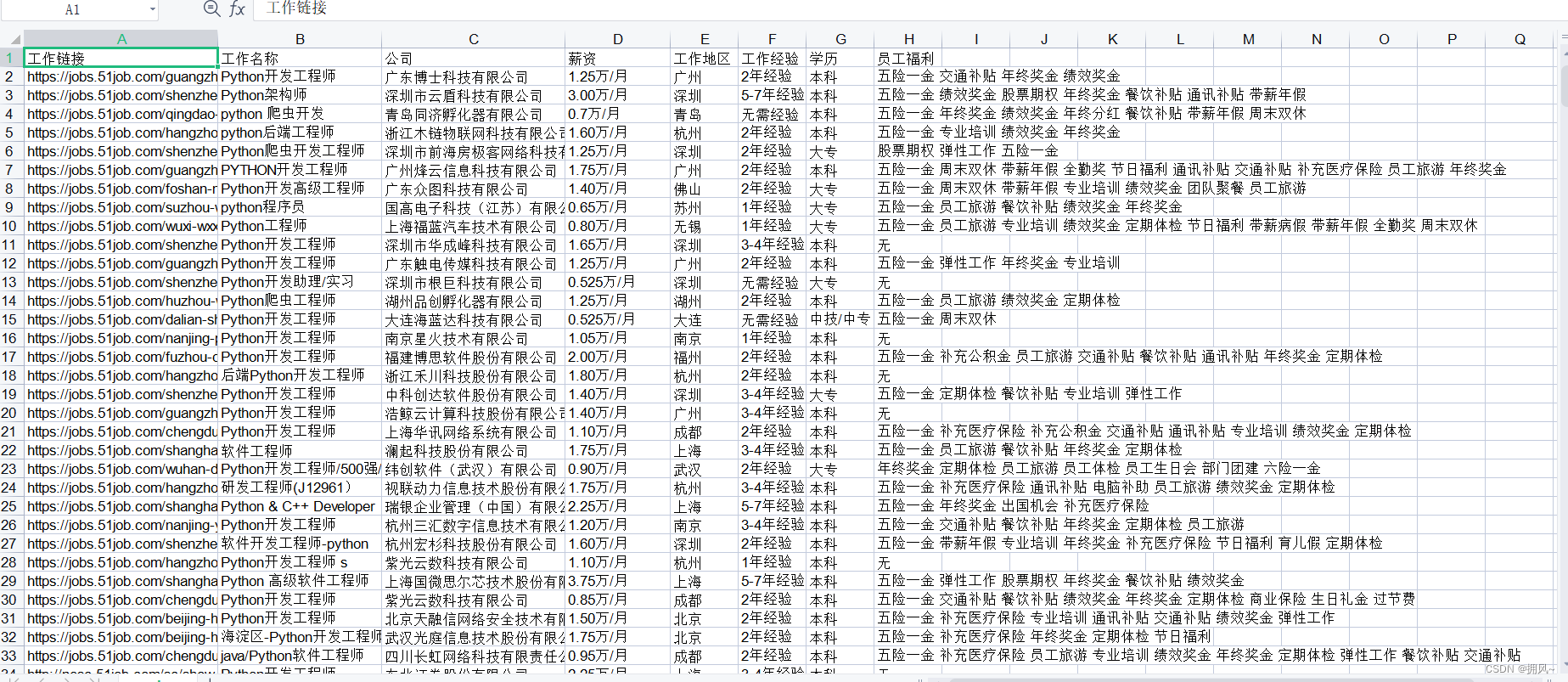
1. Save to excel
- def saveData(datalist, savepath):
- print("sava....")
- book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding="utf-8", style_compression=0) # 创建work对象
- sheet = book.add_sheet('python', cell_overwrite_ok=True) # 创建工作表
- col = ("工作链接", "工作名称", "公司", "薪资", "工作地区", "工作经验", "学历", "员工福利")
- for i in range(0, 8):
- sheet.write(0, i, col[i]) # 列名
- for i in range(0, 1000):
- # print("第%d条" %(i+1))
- data = datalist[i]
- for j in range(0, 8):
- sheet.write(i + 1, j, data[j]) # 数据
-
- book.save(savepath) # 保存数据
The results show that:
2. Save to the database
- # 创建数据表 (表名为newjob)
- def init_job(jobpath):
- sql = '''
- create table newjob
- (
- id integer primary key autoincrement,
- job_href text,
- job_name varchar,
- job_company varchar,
- job_salary text ,
- job_area varchar ,
- job_experience text,
- job_education text,
- job_fuli text
- )
- '''
- conn = sqlite3.connect(jobpath)
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- cursor.execute(sql)
- conn.commit()
- conn.close()
-
- #将数据保存到数据库中
- def saveData2DB(datalist, jobpath):
- init_job(jobpath)
- conn = sqlite3.connect(jobpath)
- cur = conn.cursor()
-
- for data in datalist:
- for index in range(len(data)):
- data[index] = '"' + str(data[index]) + '"'
- sql = '''
- insert into newjob (
- job_href,job_name,job_company,job_salary,job_area,job_experience,job_education,job_fuli)
- values(%s)''' % ",".join(data)
- # print(sql)
- cur.execute(sql)
- conn.commit()
- cur.close()
- conn.close()

3. call
in the main function
- # 保存数据到表格
- saveData(datalist, savepath)
- # 保存数据到数据库
- saveData2DB(datalist, jobpath)
3. Use flask to realize visualization
1. Main function
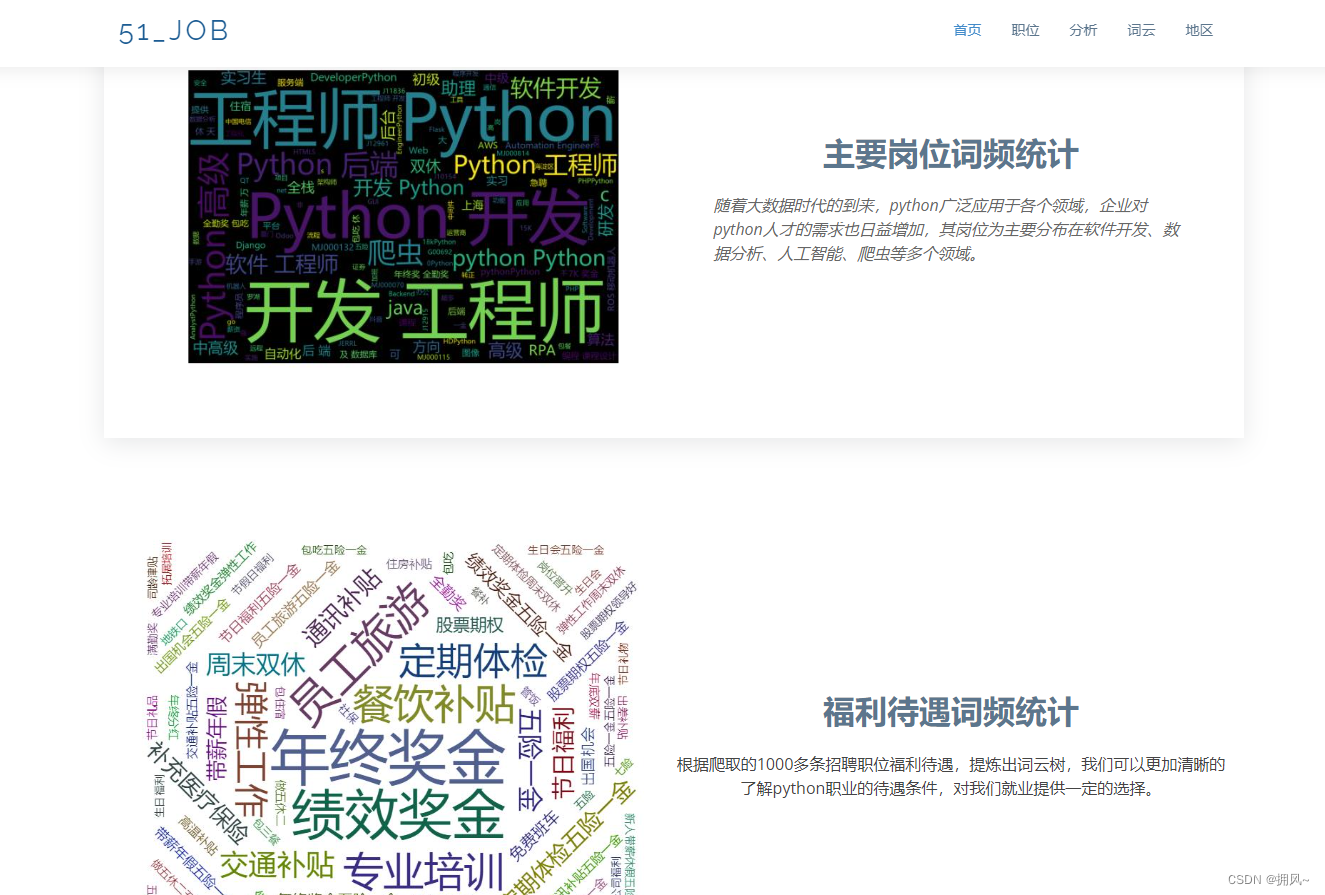
Realize drawing, word segmentation, connect to database to import data, make words, etc.
- import jieba # 分词作用
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # 绘图作用,数据可视化
- from wordcloud import WordCloud # 词云
- from PIL import Image # 图片处理
- import numpy as np # 矩阵运算
- import sqlite3 # 数据库
-
- # 准备词云所需要的词
- con = sqlite3.connect("newjob.db")
- cur = con.cursor()
- sql = "select job_name from newjob"
- data = cur.execute(sql)
- test = ""
- for item in data:
- test = test + item[0]
- # print(test)
- cur.close()
- con.close()
-
- # 分词
- cut = jieba.cut(test)
- string = " ".join(cut)
- print(len(string))
-
- img = Image.open(r'static\assets\img\demo.png') # 打开图片
- img_array = np.array(img) # 将图片转化为二维数组
- wc = WordCloud(
- background_color="white",
- mask=img_array,
- font_path="msyh.ttc" # 字体所在位置 c:\windows\fonts
- )
- wc.generate_from_text(string)
-
- # 绘制图片
- fip = plt.figure(1)
- plt.imshow(wc)
- plt.axis("off") # 是否显示坐标轴
- # plt.show() #显示生成的词云图片
-
- #输出词云图片到文件
- plt.savefig(r'static\assets\img\demo1.jpg')

2. Visual interface:
2.1 Job information display + pagination
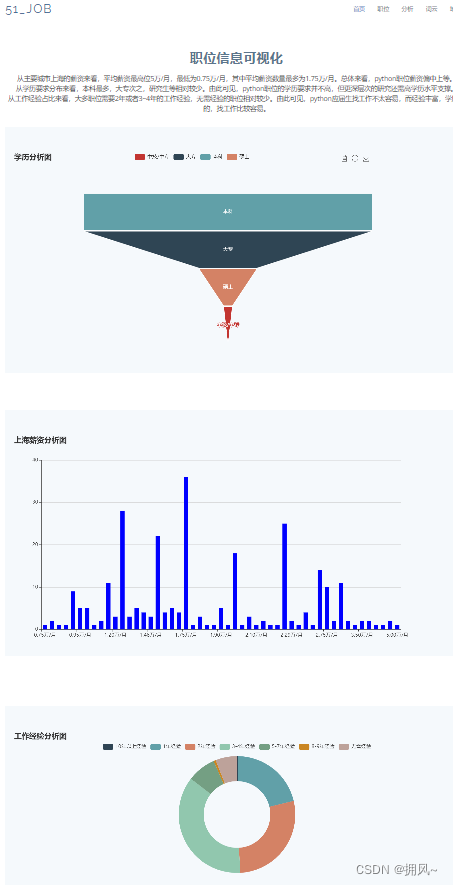
2.2 Use echars to make icons
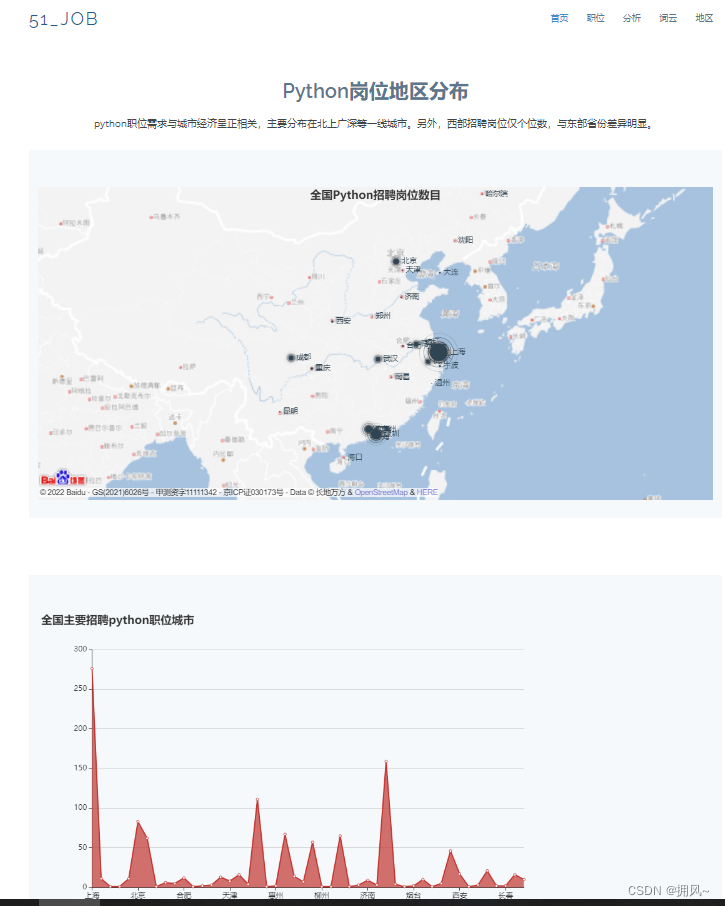
2.3 Import map
2.4 Make word cloud
- import jieba # 分词作用
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # 绘图作用,数据可视化
- from wordcloud import WordCloud # 词云
- from PIL import Image # 图片处理
- import numpy as np # 矩阵运算
- import sqlite3 # 数据库
-
- # 准备词云所需要的词
- con = sqlite3.connect("newjob.db")
- cur = con.cursor()
- sql = "select job_name from newjob"
- data = cur.execute(sql)
- test = ""
- for item in data:
- test = test + item[0]
- # print(test)
- cur.close()
- con.close()
-
- # 分词
- cut = jieba.cut(test)
- string = " ".join(cut)
- print(len(string))
-
- img = Image.open(r'static\assets\img\demo.png') # 打开图片
- img_array = np.array(img) # 将图片转化为二维数组
- wc = WordCloud(
- background_color="white",
- mask=img_array,
- font_path="msyh.ttc" # 字体所在位置 c:\windows\fonts
- )
- wc.generate_from_text(string)
-
- # 绘制图片
- fip = plt.figure(1)
- plt.imshow(wc)
- plt.axis("off") # 是否显示坐标轴
- # plt.show() #显示生成的词云图片
-
- #输出词云图片到文件
- plt.savefig(r'static\assets\img\demo1.jpg')

3. Summary
This is the first time I write a project summary, the notes are not perfect, I just made a very simple framework, just record it! (Complete project engineering documents are required, you can private message or leave a message)
Category of website: technical article > Blog
Author:cindy
link:http://www.pythonblackhole.com/blog/article/25327/deef017e559a86780075/
source:python black hole net
Please indicate the source for any form of reprinting. If any infringement is discovered, it will be held legally responsible.
name:
Comment content: (supports up to 255 characters)
no articles